Socket Sizes And Measurements Chart (Complete Guide)
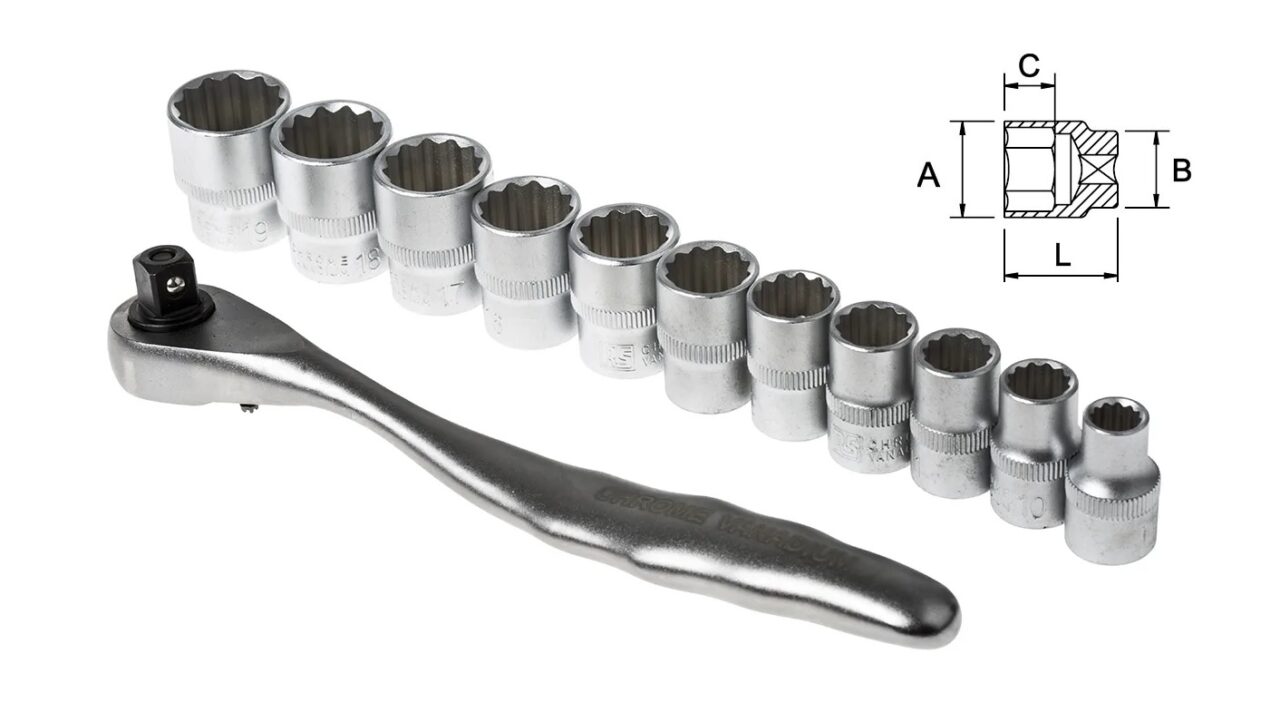

Arranging your sockets by size may seem straightforward and easy, but it’s not always that simple, especially when we have two measurement standards, such as SAE and metric. If you’ve just purchased a new set of sockets, we are here to help you organize them.
This complete guide will provide you with everything you need to know about socket types and sizes, along with a detailed measurements chart. So, let’s get started!
To properly organize your sockets, understand the three common drive sizes: 1/2″, 3/8″, and 1/4″. Each is suited for different torque levels and applications. Additionally, recognize the difference between impact sockets for high-torque tools and point sockets for precise fitting in various tasks.
Table of Contents
Common Drive Socket Sizes
When it comes to drive sockets, think of them as the square holes for attaching the socket that are used to turn a tool like a wrench or a ratchet. There are three standard sizes are used for different tasks. Here are the most popular sizes we typically use:
- 1/2″ Drives: These drives are primarily for heavy-duty jobs with large nuts requiring more force or torque. They’re commonly used with 19mm socket sizes, perfect for tasks like driving lag bolts into walls for mounting an LED TV.
- 3/8″ Drives: These versatile drives cover many jobs, making them useful at home and in workshops. We often use them for a variety of sockets and applications.
- 1/4″ Drives: These types of drives are best for low-torque jobs. They’re used for smaller sockets, up to 14mm, and are perfect for precision or interior work.
Related Article: Shower Door Repairs: Most Common Fixes
Different Types of Sockets
Different jobs require different types of sockets. If you’re doing some mechanical jobs, the following information will be useful for you:
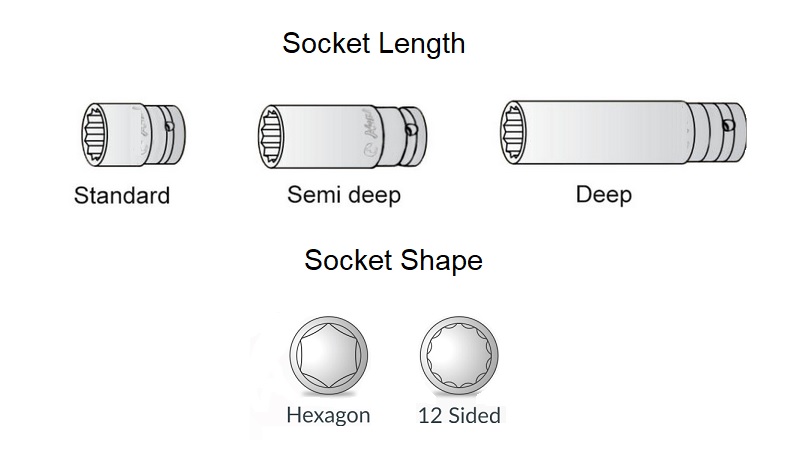
The picture above shows all the types of different sockets that you can find.
- Impact Sockets: These sockets are designed for use with pneumatic or electric wrenches, making them perfect for high-torque applications. They are much sturdier and more robust than conventional sockets, ensuring they can withstand the demands of power tools.
- Point Sockets: There are two main types: 12-point and 6-point sockets. The 12-point sockets are easy to fit and use, making them great for light household tasks. On the other hand, 6-point sockets are used for heavy-duty jobs requiring substantial torque. They are less likely to slip and are considered more durable.
Shallow vs. Deep Sockets
Shallow sockets, also known as normal sockets, can sometimes make jobs difficult if the bolt hits the end of the socket before the nut is fully engaged. In these cases, deep sockets are the solution. Measuring about an inch in length, deep sockets can reach nuts in inaccessible places, provided your driver has an extension.
By understanding these types and sizes, we ensure we always have the right socket for the job. Whether you’re tackling a heavy-duty project or a precision task, having a well-organized and comprehensive socket set is essential.
Metric Socket Sizes Chart
A metric socket chart is a great tool for anyone who is working with fasteners that adhere to the metric system. It provides a clear and organized display of socket sizes, making identifying the correct tool for each specific task easier. Here is a full table with metric socket sizes:
| 3/8″ Drive | 1/4″ Drive | 3/4″ Drive | 1/2″ Drive |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5.5mm | 4mm | 19mm | 8mm |
| 6mm | 4.5mm | 20mm | 9mm |
| 7mm | 5mm | 21mm | 10mm |
| 8mm | 5.5mm | 22mm | 11mm |
| 9mm | 6mm | 23mm | 12mm |
| 10mm | 7mm | 24mm | 13mm |
| 11mm | 8mm | 25mm | 14mm |
| 12mm | 9mm | 26mm | 15mm |
| 13mm | 10mm | 27mm | 16mm |
| 14mm | 11mm | 28mm | 17mm |
| 15mm | 12mm | 29mm | 18mm |
| 16mm | 13mm | 30mm | 19mm |
| 17mm | 14mm | 31mm | 20mm |
| 18mm | 15mm | 32mm | 21mm |
| 19mm | 33mm | 22mm | |
| 20mm | 34mm | 23mm | |
| 21mm | 35mm | 24mm | |
| 22mm | 36mm | 25mm | |
| 38mm | 26mm | ||
| 40mm | 27mm | ||
| 41mm | 28mm | ||
| 42mm | 30mm |
SAE Socket Sizes Chart

Understanding SAE socket sizes is also important for anyone who is involved in mechanical work or DIY projects. These measurements are handy when it comes to selecting the right tools and ensuring a good fit for various tasks. Here is a full table of SAE socket sizes:
| 3/8″ Drive | 1/4″ Drive | 3/4″ Drive | 1/2″ Drive |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1/4″ | 5/32″ | 7/8″ | 3/8″ |
| 5/16″ | 3/16″ | 15/16″ | 7/16″ |
| 3/8″ | 7/32″ | 1″ | 1/2″ |
| 7/16″ | 1/4″ | 1-1/16″ | 9/16″ |
| 1/2″ | 9/32″ | 1-1/8″ | 19/32″ |
| 9/16″ | 5/16″ | 1-3/16″ | 5/8″ |
| 5/8″ | 11/32″ | 1-1/4″ | 21/32″ |
| 11/16″ | 3/8″ | 1-5/16″ | 11/16″ |
| 3/4″ | 7/16″ | 1-3/8″ | 3/4″ |
| 13/16″ | 1/2″ | 1-7/16″ | 25/32″ |
| 7/8″ | 9/16″ | 1-1/2″ | 13/16″ |
| 15/16″ | 1-5/8″ | 7/8″ | |
| 1″ | 1-11/16″ | 15/16″ | |
| 1-3/4″ | 1″ | ||
| 1-13/16″ | 1-1/16″ | ||
| 1-7/8″ | 1-1/8″ | ||
| 2″ | 1-3/16″ | ||
| 2-1/8″ | 1-1/4″ | ||
| 2-3/16″ | 1-1/2″ | ||
| 2-1/4″ |
SAE to Metric Socket Conversion Chart
Sometimes, you might find yourself with a wrench measured in metric units and a nut in Imperial units, and you don’t know if it will fit. Understanding how to convert between these units accurately is essential. The chart provided below will assist you in effortlessly converting dimensions from SAE to Metric and vice versa.
| SAE Size | Metric Size | Inches Decimal | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5/32″ | 0.156 | 5/32″ and 4mm are | |
| 4mm | 0.157 | close enough | |
| 4.5mm | 0.177 | ||
| 3/16″ | 0.188 | ||
| 5mm | 0.197 | ||
| 5.5mm | 0.216 | ||
| 7/32″ | 0.219 | ||
| 6mm | 0.236 | ||
| 1/4″ | 0.25 | ||
| 6.5mm | 0.256 | ||
| 7mm | 0.276 | ||
| 9/32″ | 0.281 | ||
| 5/16″ | 0.313 | 5/16″ and 8mm are | |
| 8mm | 0.315 | close enough | |
| 11/32″ | 0.344 | ||
| 9mm | 0.354 | ||
| 3/8″ | 0.375 | ||
| 10mm | 0.394 | ||
| 13/32″ | 0.406 | ||
| 11mm | 0.433 | 7/16″ and 11mm are | |
| 7/16″ | 0.438 | close enough | |
| 15/32″ | 0.469 | 15/32″ and 12mm are | |
| 12mm | 0.472 | close enough | |
| 1/2″ | 0.5 | ||
| 13mm | 0.512 | ||
| 17/32″ | 0.531 | ||
| 14mm | 0.551 | ||
| 9/16″ | 0.563 | ||
| 15mm | 0.591 | 19/32″ and 15mm are | |
| 19/32″ | 0.594 | close enough | |
| 5/8″ | 0.625 | ||
| 16mm | 0.63 | ||
| 21/32″ | 0.656 | ||
| 17mm | 0.669 | ||
| 11/16″ | 0.688 | ||
| 18mm | 0.709 | ||
| 23/32″ | 0.719 | ||
| 19mm | 0.748 | 3/4″ and 19mm are | |
| 3/4″ | 0.75 | close enough | |
| 25/32″ | 0.781 | ||
| 20mm | 0.787 | ||
| 13/16″ | 0.813 | ||
| 21mm | 0.827 | ||
| 27/32″ | 0.844 | ||
| 22mm | 0.866 | ||
| 7/8″ | 0.875 | ||
| 23mm | 0.906 | 29/32″ and 23mm are | |
| 29/32″ | 0.906 | close enough | |
| 15/16″ | 0.938 | ||
| 24mm | 0.945 | ||
| 1″ | 1 |
If you want to learn more about this topic, be sure to watch this YouTube video:
Related Article: How To Fix Steep Stairs Little Headroom (4 Great Ways)
FAQ: People Also Ask
What socket sizes do I need for my project?
Choose the appropriate drive size of ratchets and sockets based on the bolt or nut diameter. For fasteners close to 1/4″ or 6mm, opt for a 1/4″ drive, and for those around 3/8″ or 10mm, a 3/8″ drive is suitable.
What are the typical uses of standard socket sizes?
Standard socket sizes are measured by the socket wrench’s opening and are crafted to accommodate various nut or bolt sizes. Typically, the sizes range from 1/4 inch to 1 inch, covering most general needs, with additional specific sizes for more unique tasks.
What size socket is commonly needed for lug nuts?
Lug nuts commonly require socket sizes of 17 mm, 19 mm, 21 mm, and 22 mm in metric measurements, along with 11 16-inch, 3/4-inch, 13 16-inch, and 7/8-inch in SAE measurements.
What socket do I need to change a tire?
When changing a tire, a lug wrench, a specific socket wrench, is typically used to loosen the lug nuts. Using the right tools and adhering to safety guidelines is crucial during this process.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, understanding socket sizes and their use is important for any mechanical task, whether you’re a professional or a DIY enthusiast. Properly organizing your socket set and knowing when to use specific sizes and types will save time and effort.
By selecting the right socket for your needs, you ensure efficiency and safety in your work. Always refer to a detailed conversion chart and guidelines to make informed decisions and achieve the best results. I hope that this article has helped you. If you have any additional questions, feel free to comment below.