How Does a Mechanical Thermostat Work?
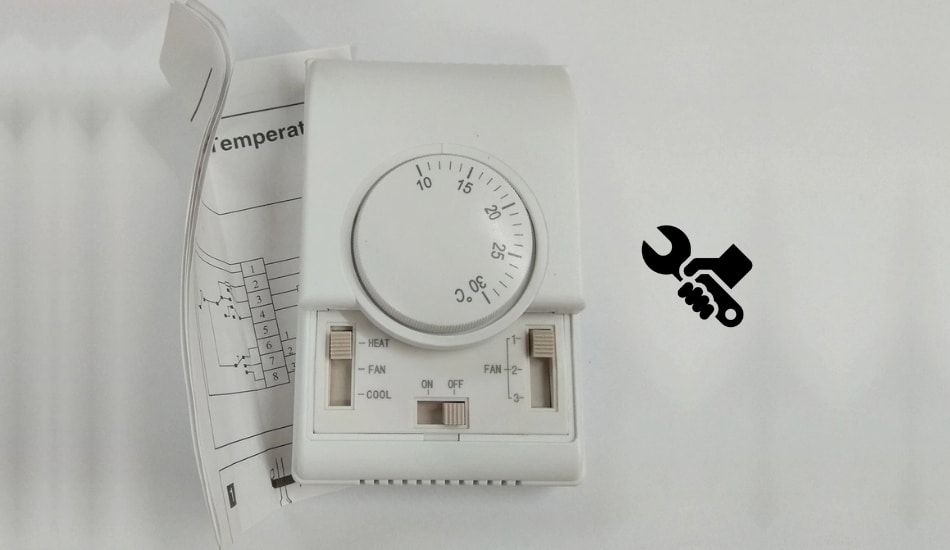

A mechanical thermostat is quite often used in heating systems such as private houses, but also in ordinary residential apartments. Moreover, their various varieties can control the operation of almost any climate systems – air conditioners, underfloor heating, water heaters, etc., making the space around us as comfortable and convenient as possible for living. Let’s take a closer look to see how a mechanical thermostat works, its structure, and where it is all used.
Table of Contents
How Does a Mechanical Thermostat Work?
So How Does a Mechanical Thermostat Work? A mechanical thermostat is a device that regulates the heat with the help of the expansion of their internal metallic strips. When the strip is cool, the circle is closed, and electricity goes through the connected circuit which leads to switching on the heating. When the strip heats up, it opens the circuit and switches off the heating, which leads to cooling the room down.
Heating your home to enjoy a certain level of comfort is essential during the winter. But heating your home properly while avoiding exploding your energy bill is even better. To do this, you can opt for the installation of a thermostat, which will ensure the most constant temperature possible to heat your home. At a time when the electronic thermostat is used more and more, does the mechanical thermostat still have an interest? Let’s find out!
Working Principle
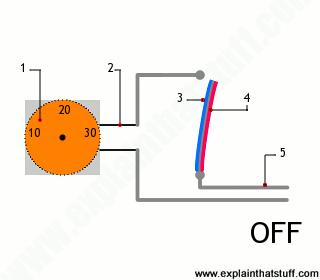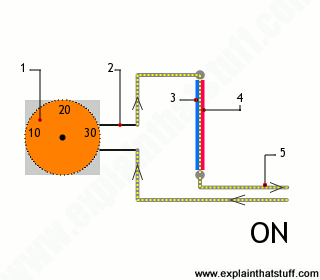
- An outer dial for setting the temperature.
- The thermostat dial is connected through a circuit to the temperature sensor.
- There are two separate metal strips fastened together: a piece of iron (red) bolted to a piece of brass (blue).
- Iron expands less than brass as it gets hotter, so the bimetal strip curves inward as the temperature rises.
- When the strip is cool the heating is ON. When the strip is hotter, the circuit is off, which leads to cooling the room down.
Where Mechanical Thermostat is Used Today?
The mechanical thermostat, sometimes also called a manual thermostat, is a kind of power switch that helps ensure your comfort in your home by regulating the temperature. It can be used both for heating and cooling an apartment or house.

The main difference between room mechanical thermostats and thermostats of another type is that it is a separate, completely independent device, most often made in the form of an external wiring product, intended for indoor installation.
Simply put, a mechanical thermostat, depending on the set program, by turning it on or off certain heating or cooling devices, maintains the required temperature in the room. The main feature of the mechanical thermostat is the complete absence of electrical power, i.e. no power is required for its operation, not even batteries. How does a mechanical thermostat work, what exactly allows it to measure the temperature of the surrounding space and control electrical appliances?
If you want to know How Analog Thermostat Works, check out this post!
The Operating Principle of Mechanical Thermostat
Mechanical thermostats have one single principle in the operation, and that is the ability of some materials and substances to change their mechanical properties depending on temperature.

As an everyday example, familiar to everyone, that would explain the principle of operation of a mechanical thermostat, we can cite an ordinary mercury thermometer, with which we measure body temperature. The mercury contained inside the thermometer increases in volume with increasing temperature and enters the graduated capillary, thereby showing the exact temperature.
Roughly the same processes take place in a mechanical thermostat, the only difference is that a change in temperature to a certain level, which is indicated by us separately by a regulating wheel, starts certain processes, most often closes or breaks an electrical circuit, what causes turning on or off heating devices.
To make it clearer how it all works, let’s look at the design of a standard room mechanical thermostat.
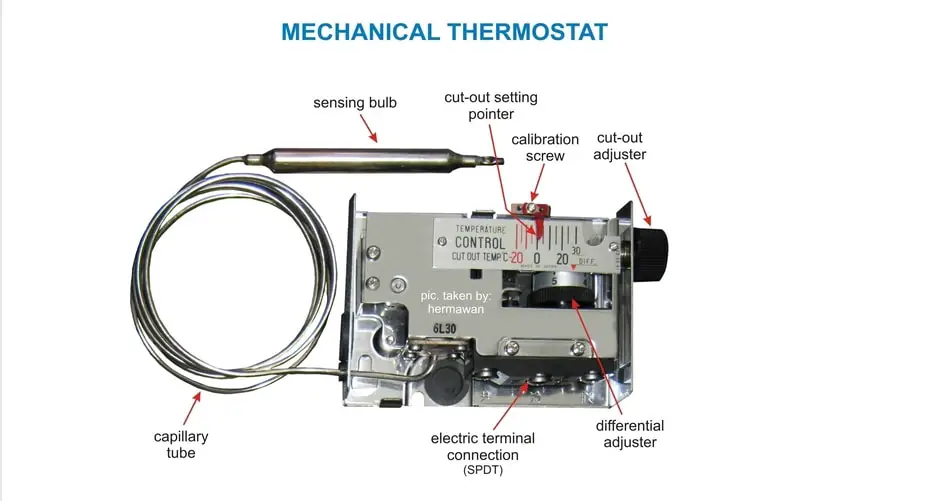
Mechanical Thermostat Parts
The main structural element of almost any room mechanical thermostat is a gas membrane. By the way, this is also the reason why they are often called membrane thermostats.

The special gas inside the membrane, when the temperature changes, changes its volume, thereby acting on the membrane walls. Which, when changing, trigger the mechanism for closing or opening the electrical circuit that feeds the heating or cooling system.
The choice of just such a device method for a room thermostat is due to the possibility of organizing a simple way to adjust its response temperature, as well as the fact that the device responds precisely to changes in the air temperature, and not the surface, which is most important in heating and cooling systems.
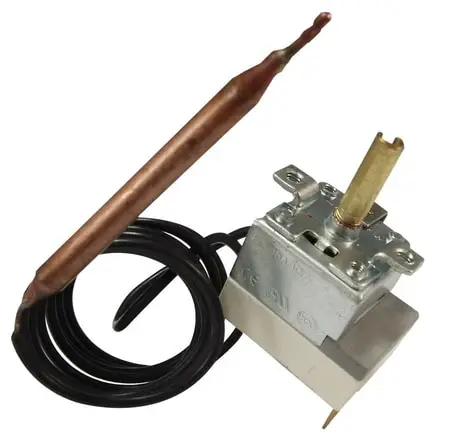

Therefore, for example, for underfloor heating, it is more reasonable to use mechanical liquid thermostats with a remote sensor. The control of the response temperature of the membrane room thermostat is carried out using a dial, which is connected to the membrane mechanism.
By turning the wheel, we move closer or further the walls of the membrane from the control mechanism, thereby changing the temperature at which the electrical circuit will close or open.
In other words, if the triggering mechanism is closer to the membrane wall, then the gas located in it needs to slightly change the volume for it to trigger; accordingly, a lower temperature is needed and vice versa. This is how the adjusting wheel works.
Let’s look at exactly how you can apply a mechanical thermostat to the heating system of a house or apartment.
Using a Mechanical Thermostat in Heating
Most often, room mechanical thermostats are used for heating the houses, together with gas boilers. Manufacturers quite often in the design of boilers provide for a connection diagram through a mechanical thermostat. The device is installed in a break in the supply wire leading to the boiler and in the case when the air temperature in the room drops below the set threshold value, the circuit closes and the gas boiler starts up, starting to heat the room, maintaining the temperature of the coolant.
In exactly the same way, home thermostats are connected to any electric heaters in rooms, be they oil heaters, infrared heaters, or any other used for heating indoor air. Thus, the heating process becomes fully automated, requiring almost no human participation in its work, after it is adjusted.
There are a lot of possible options for using mechanical thermostats; in heating automation, it is simply irreplaceable because of its simplicity and reliability. And the simplicity of the design allows manufacturers to produce room mechanical thermostats at a much lower cost than electronic ones, which is an important part of their popularity with the consumer.
Selecting a Mechanical Thermostat
Currently, there are a lot of manufacturers of mechanical thermostats. There are models and famous brands, but, most often, you will find unfamiliar, and unknown names on sale. In my practice I have used a large number of different mechanical thermostats and can advise the following:
When choosing, be sure to pay attention to the maximum switching power. If it is written that the thermostat is 10 Amperes, it will be possible to connect a load of no more than 2.2-2.3 kW to it. Thermostats with more than 3.6 kW of connected power are rare. If you need to connect more power, you will have to use a contractor, according to the connection diagram. Of the inexpensive thermostats, I liked this one – BALLU BMT-1 – you can buy it here. By design, it is completely similar to that described in this article. It will work for you for exactly 3-5 years, and then it depends on the build quality of a particular model and operating conditions. For a summer residence, a garage – that’s it!
Do Mechanical Thermostats Have The Future?
As we have said, currently, the mechanical thermostat is less and less chosen by individuals, who prefer more innovative and more complete installations. For example, the smart thermostat can now be controlled remotely, control other electrical devices, or even better understand the amount of energy you consume in your home. Things a mechanical thermostat can’t do.
That being said, the mechanical thermostat can come in very handy in certain situations. This is for example the case for the operation of a heating device supplied by an unstable electrical source or even provided with a relay. In this context, this type of thermostat will remain safe from electric grilling, which cannot be guaranteed with regard to an electronic or connected thermostat.
Also, it should be remembered that, whatever the situation, the installation of a mechanical thermostat has two not insignificant advantages: on the one hand, it improves the thermal comfort of everyone in the home by guaranteeing an ideal temperature in the latter and, on the other hand, it allows energy savings, thanks to an optimized heating consumption.
Even this thermostats don’t have the future, you can see my article about How Smart Thermostats Save Money.
Save Money by Choosing the Right Offer
In addition to betting on a mechanical thermostat to regulate your heating consumption and thus achieve your daily energy savings, it is important to know that the choice of your energy supplier also has direct and not insignificant consequences on the amount of your energy bill.
Final Thoughts
The mechanical thermostat is still present in many homes today, but it is less popular than the electronic or smart thermostat. In addition, mechanical thermostats are useful in homes thanks to its very simple, precise, and particularly effective use. I hope this article helped you. If you need advice on choosing a mechanical thermostat model – write in the comments, I will try to help with advice!